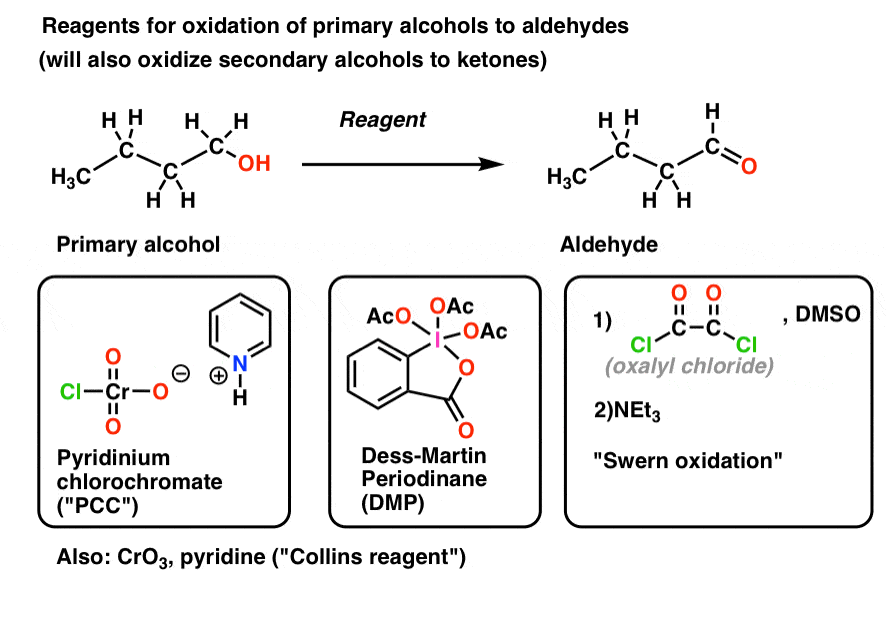
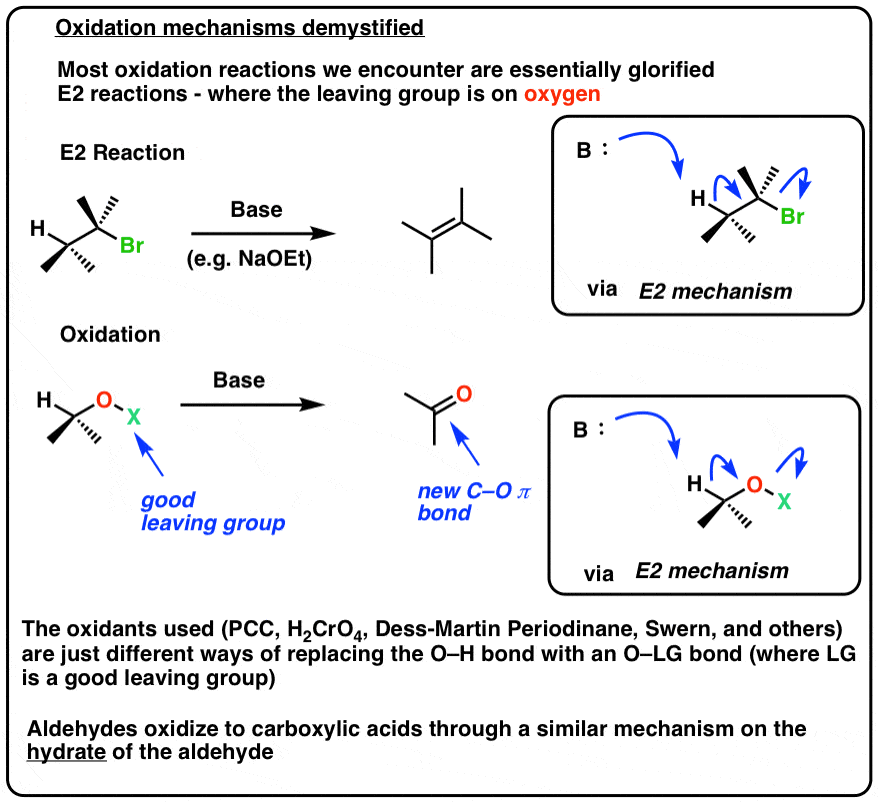
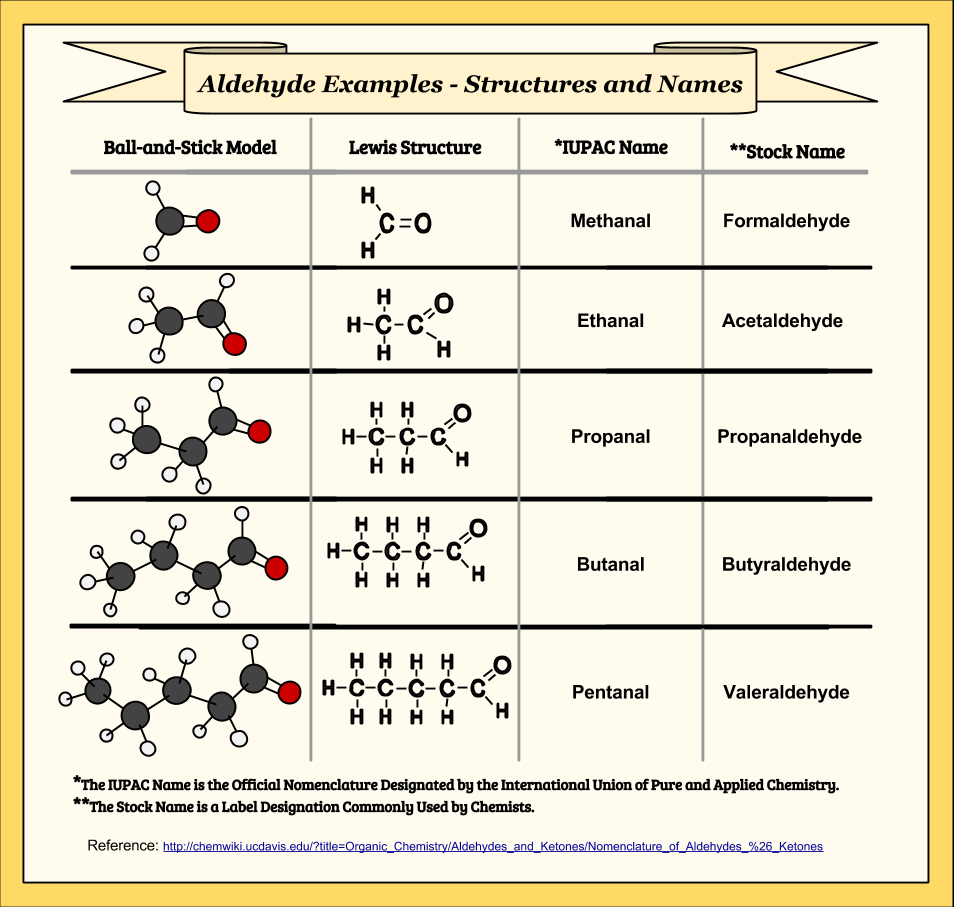
Aldehydes May Oxidize To Form
Aldehydes May Oxidize To Form - Web oxidation can be achieved by heating the alcohol with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate. In this process, the hydroxy hydrogen of the alcohol is replaced by a leaving group (x in. Hence, option b is correct. Web the oxidation of aldehydes by o2 appears to be a chain mechanism involving free radicals and yielding a rather reactive peracid, which then reacts with the. O c h o c o h oxidation ¥alcohols. Ketones are not oxidised under these conditions as they lack the critical h for the elimination to occur (see. Web ¥carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones may be oxidized to form compounds at the next òoxidation level ó, that of carboxylic acids. Web the product of the oxidation of an aldehyde, results in a carboxylic acid. Because the solution is alkaline, the aldehyde itself is oxidized to a salt of the corresponding carboxylic acid. Web aldehydes undergo oxidation more quickly than ketones.
Because the solution is alkaline, the aldehyde itself is oxidized to a salt of the corresponding carboxylic acid. This will happen if the oxidation happens under acidic or alkaline conditions. Hence, option b is correct. They use a strong oxidant like potassium permanganate (kmno4) Web oxidation of 1 o alcohols to form aldehydes (section 17.7) pcc pyridinium chlorochromate ( pcc) is a milder version of chromic acid. Web depending on the conditions of the oxidation, aldehydes will form carboxylic acids. O c h o c o h oxidation ¥alcohols. Web the oxidation of an alcohol to form an aldehyde or ketone is very important in synthesis. Web aldehydes, rcho, can be oxidised to carboxylic acids, rco2h. These functional groups are useful for further reactions;
Web oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. Web answer 1 aldehydes are a class of organic compound which can be oxidized to form corresponding carboxylic acid or organic acid. Web ¥carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones may be oxidized to form compounds at the next òoxidation level ó, that of carboxylic acids. In this process, the hydroxy hydrogen of the alcohol is replaced by a leaving group (x in. In this case, excess dichromate will further oxidize the aldehyde to a. This will happen if the oxidation happens under acidic or alkaline conditions. Ketones are not oxidised under these conditions as they lack the critical h for the elimination to occur (see. These functional groups are useful for further reactions; Web currently, most investigations on aldehyde oxidations focus on aerobic oxidation, i.e., using molecular oxygen (o 2) to oxidize aldehydes into the corresponding carboxylic. Web aldehydes undergo oxidation more quickly than ketones.
Alcohol Oxidation Mechanisms and Practice Problems Chemistry Steps
Web there are some reagents which can selectively oxidize a primary alcohol and stop at an aldehyde without complete oxidation to the acid. Primary alcohols can only be oxidized to form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.for instance, using chromic acid (to get a carboxylic acid), or using pcc in. In this case, excess dichromate will further oxidize the aldehyde to a..
Solved Be sure to answer all parts. Hydroxy aldehydes A and
This will happen if the oxidation happens under acidic or alkaline conditions. In this process, the hydroxy hydrogen of the alcohol is replaced by a leaving group (x in. Web oxidation of 1 o alcohols to form aldehydes (section 17.7) pcc pyridinium chlorochromate ( pcc) is a milder version of chromic acid. Because the solution is alkaline, the aldehyde itself.
Alcohol Oxidation "Strong" & "Weak" Oxidants Master Organic Chemistry
Web aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted, allowing them to be easily oxidized to form carboxylic acids. Web aldehydes undergo oxidation more quickly than ketones. Web aldehydes reduce the diamminesilver(i) ion to metallic silver. Web oxidation of 1 o alcohols to form aldehydes (section 17.7) pcc pyridinium chlorochromate ( pcc) is a milder.
PDF Télécharger aldehydes may oxidize to form Gratuit PDF
Web depending on the conditions of the oxidation, aldehydes will form carboxylic acids. Web the oxidation of aldehydes by o2 appears to be a chain mechanism involving free radicals and yielding a rather reactive peracid, which then reacts with the. Hence, option b is correct. Primary alcohols can only be oxidized to form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.for instance, using chromic.
Representative examples of oxidation of aldehydes. Download
Web aldehydes reduce the diamminesilver(i) ion to metallic silver. Web aldehydes, rcho, can be oxidised to carboxylic acids, rco2h. Web the product of the oxidation of an aldehyde, results in a carboxylic acid. Web aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted, allowing them to be easily oxidized to form carboxylic acids. Web oxidation of.
Tollens Reagent Silver Mirror Test for Aldehydes
In this case, excess dichromate will further oxidize the aldehyde to a. Web aldehydes reduce the diamminesilver(i) ion to metallic silver. Web the product of the oxidation of an aldehyde, results in a carboxylic acid. Web aldehydes undergo oxidation more quickly than ketones. Web oxidation can be achieved by heating the alcohol with an acidified solution of potassium dichromate.
Pathways leading to formation of oxidation and nitric oxide (NO
Web the oxidation of an alcohol to form an aldehyde or ketone is very important in synthesis. O c h o c o h oxidation ¥alcohols. Web aldehydes reduce the diamminesilver(i) ion to metallic silver. Web there are some reagents which can selectively oxidize a primary alcohol and stop at an aldehyde without complete oxidation to the acid. These functional.
PPT Aldehydes, Ketones, and carboxylic acids PowerPoint Presentation
Web oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. In this process, the hydroxy hydrogen of the alcohol is replaced by a leaving group (x in. These functional groups are useful for further reactions; Hence, option b is correct. Web the oxidation of an alcohol to form an aldehyde or ketone is very important in synthesis.
Organic Chemistry, Form, Part 14 Aldehydes Structure and
Web aldehydes reduce the diamminesilver(i) ion to metallic silver. In this case, excess dichromate will further oxidize the aldehyde to a. Web oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones. Web depending on the conditions of the oxidation, aldehydes will form carboxylic acids. Oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes is partial oxidation;
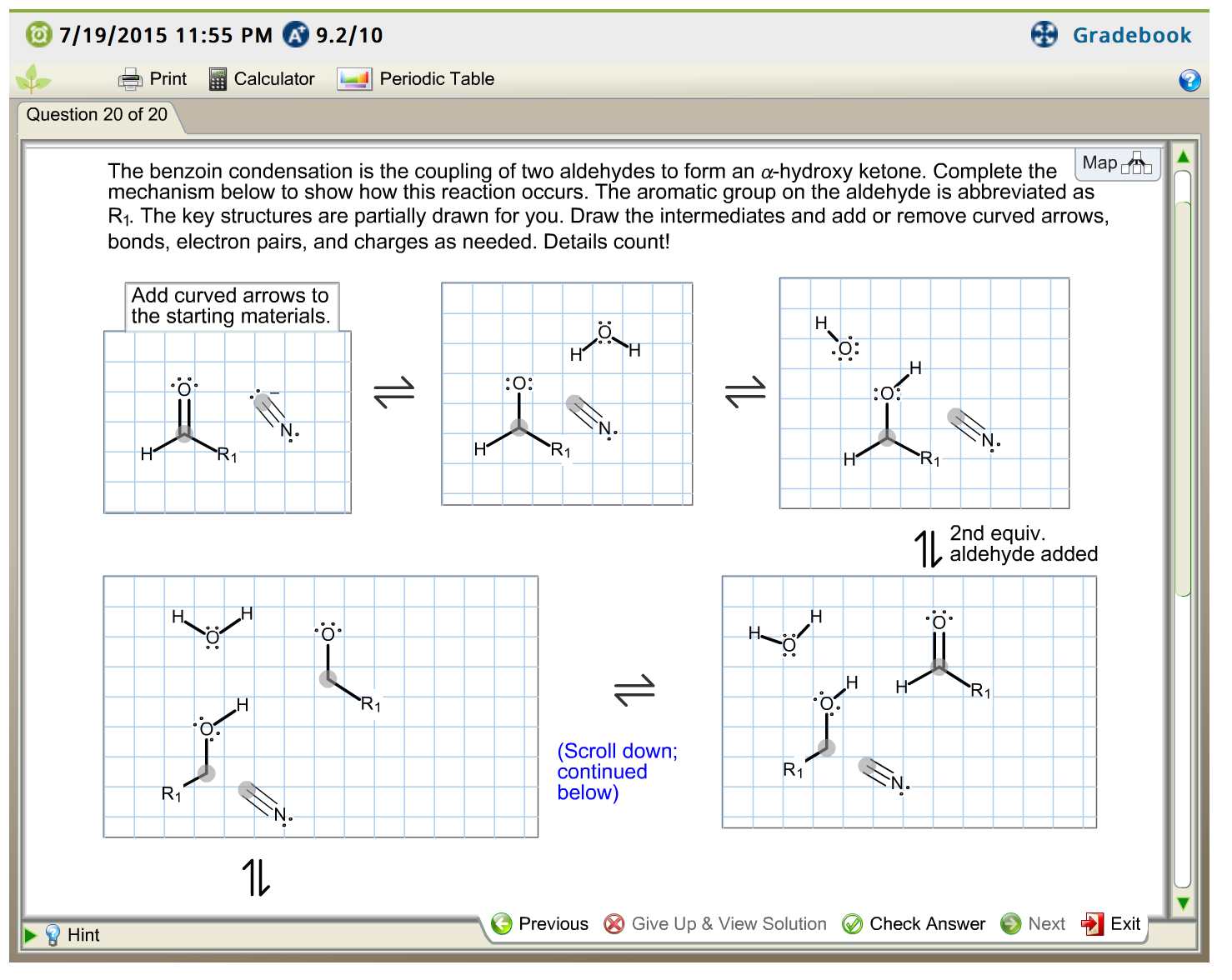
Solved The benzoin condensation is the coupling of two
In this case, excess dichromate will further oxidize the aldehyde to a. Web aldehydes undergo oxidation more quickly than ketones. Web there are some reagents which can selectively oxidize a primary alcohol and stop at an aldehyde without complete oxidation to the acid. Web depending on the conditions of the oxidation, aldehydes will form carboxylic acids. Oxidation of alcohols to.
Ketones Are Not Oxidised Under These Conditions As They Lack The Critical H For The Elimination To Occur (See.
Web depending on the conditions of the oxidation, aldehydes will form carboxylic acids. They use a strong oxidant like potassium permanganate (kmno4) This will happen if the oxidation happens under acidic or alkaline conditions. Hence, option b is correct.
Web Oxidation Can Be Achieved By Heating The Alcohol With An Acidified Solution Of Potassium Dichromate.
These functional groups are useful for further reactions; In this process, the hydroxy hydrogen of the alcohol is replaced by a leaving group (x in. Web oxidation of 1 o alcohols to form aldehydes (section 17.7) pcc pyridinium chlorochromate ( pcc) is a milder version of chromic acid. Web aldehydes undergo oxidation more quickly than ketones.
Web Aldehydes Reduce The Diamminesilver(I) Ion To Metallic Silver.
In this case, excess dichromate will further oxidize the aldehyde to a. Web currently, most investigations on aldehyde oxidations focus on aerobic oxidation, i.e., using molecular oxygen (o 2) to oxidize aldehydes into the corresponding carboxylic. Because the solution is alkaline, the aldehyde itself is oxidized to a salt of the corresponding carboxylic acid. Web oxidation of alcohols to aldehydes and ketones.
Web There Are Some Reagents Which Can Selectively Oxidize A Primary Alcohol And Stop At An Aldehyde Without Complete Oxidation To The Acid.
Alcohols may be oxidized to give ketones, aldehydes, and carboxylic acids. In other words, aldehydes are better at reducing than ketones due to the presence of the hydrogen. Web the oxidation of aldehydes by o2 appears to be a chain mechanism involving free radicals and yielding a rather reactive peracid, which then reacts with the. Primary alcohols can only be oxidized to form aldehydes or carboxylic acids.for instance, using chromic acid (to get a carboxylic acid), or using pcc in.