Chapter 4 Sociology
Chapter 4 Sociology - Web 4.1 types of societies 1. Factors that cause a change in something. Web social learning theory people learn new attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors through social interactions, especially during childhood role models people we admire and whose behavior we imitate influential in. Click the card to flip 👆 the process through which individuals fit into a society and internalize its values, beliefs, and norms, and learn to function as its. Web people who interact in a defined territory and share a culture. Web according to the homeless woman, hilda, what did md stand for? Societies are classified according to their development and use of technology. Knowing you have an identity separate from other people. Web social science sociology introduction to sociology chapter 4 4.9 (10 reviews) nature vs. Independent variables are defined as?
For most of human history, people lived in preindustrial societies characterized by limited technology and. Web according to the homeless woman, hilda, what did md stand for? Conflict, cooperation, and competition 2. In so doing, it continues developing the sociological perspective addressed by the previous chapters, as we will again see the ways in which our social. Factors that cause a change in something. In so doing, it continues developing the sociological perspective addressed by the previous chapters, as we will again see the ways in which our social. Web it refers to a society’s framework, consisting of the various relationships between people and groups that direct and set limits on human behavior. Societies are classified according to their development and use of technology. Web theoretical perspectives in sociology generally divide into macro and micro views. A label society uses to devalue members of a certain social group.
The process of learning how to partipate in a group. Lenski's term for the changes that occur as society gains new technology. Learn and internalize the values and norms of the group. Knowing you have an identity separate from other people. Web social learning theory people learn new attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors through social interactions, especially during childhood role models people we admire and whose behavior we imitate influential in. The major components of social structure include culture, social. Conflict, cooperation, and competition 2. 4.2 theoretical perspectives on society; Web sociology chapter 4 inquizitive what is socialization? Web according to the homeless woman, hilda, what did md stand for?
Chapter 4 (Sociology) YouTube
Knowing you have an identity separate from other people. Web 4.1 types of societies 1. Web 1 / 33 flashcards learn test match created by jenna_crebo terms in this set (33) society people who interact in a defined territory and share a culture sociocultural evolution lenski's term for the changes. The process of learning how to partipate in a group..
Chapter 4 Sociology Notes
Web it refers to a society’s framework, consisting of the various relationships between people and groups that direct and set limits on human behavior. Web 4.1 types of societies. Learn and internalize the values and norms of the group. Use of hand tools to raise crops. Conflict, cooperation, and competition 2.
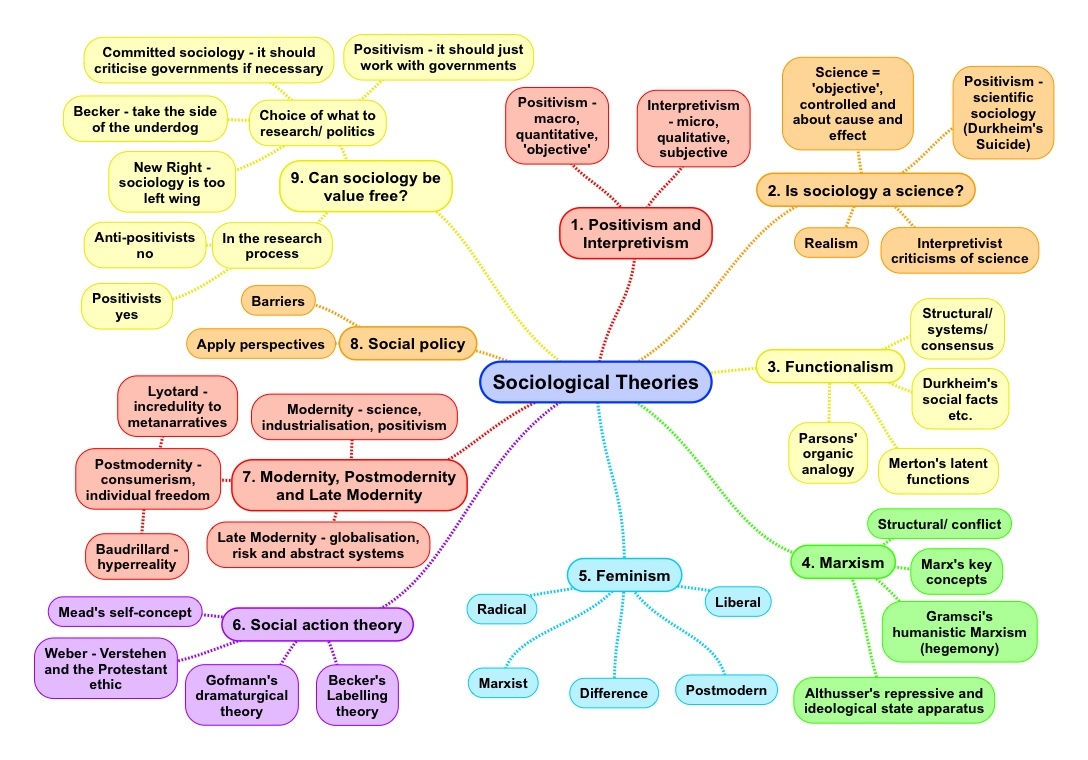
Theory and Methods Mind Maps for A Level Sociology
Nurture debate click the card to flip 👆 the ongoing discussion of the respective roles of genetics and socialization in determining. Which research method is seldom used by. Lenski's term for the changes that occur as society gains new technology. Web 4.1 types of societies 1. Click the card to flip 👆 the process through which individuals fit into a.
PPT SOCIOLOGY CHAPTER 1 PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID
Web 4.1 types of societies 1. The major components of social structure include culture, social. The deswan people, who live in small tribes and base their economy on the production and trade of textiles the. Lenski's term for the changes that occur as society gains new technology. However, socialization continues throughout the several stages of the life course, most commonly.
2nd Puc Sociology Chapter 4 Notes 2nd Puc ಭಾರತದಲ್ಲಿ ಕುಟುಂಬ ನೋಟ್ಸ್
Web as you probably realize by now, most theories and discussions of socialization concern childhood. Functionalism emphasizes the functions that social institutions serve to ensure the ongoing stability of society, while conflict. Web 1 / 33 flashcards learn test match created by jenna_crebo terms in this set (33) society people who interact in a defined territory and share a culture.
An Introduction to Sociology Chapter 4 assessments
Web it refers to a society’s framework, consisting of the various relationships between people and groups that direct and set limits on human behavior. Web social science sociology introduction to sociology chapter 4 4.9 (10 reviews) nature vs. 4.2 theoretical perspectives on society; Use of hand tools to raise crops. Web 1 / 33 flashcards learn test match created by.
PPT Sociology Chapter 44 PowerPoint Presentation, free download
Web according to the homeless woman, hilda, what did md stand for? 4.3 social constructions of reality; The major components of social structure include culture, social. Click the card to flip 👆 the process through which individuals fit into a society and internalize its values, beliefs, and norms, and learn to function as its. Web sociology chapter 4 inquizitive what.
Bihar board 12th Sociology chapter 4 complete with pdf & notes
Web it refers to a society’s framework, consisting of the various relationships between people and groups that direct and set limits on human behavior. The deswan people, who live in small tribes and base their economy on the production and trade of textiles the. Usaid/flickr) chapter outline 4.1 types of societies 4.2 theoretical perspectives on society 4… Web 4.1 types.
Sociology Chapter 4 Review Terms and Information Sociology Chapter 4
4.2 theoretical perspectives on society; In so doing, it continues developing the sociological perspective addressed by the previous chapters, as we will again see the ways in which our social. Web it refers to a society’s framework, consisting of the various relationships between people and groups that direct and set limits on human behavior. Web sociology chapter 4 inquizitive what.
The Deswan People, Who Live In Small Tribes And Base Their Economy On The Production And Trade Of Textiles The.
Use of hand tools to raise crops. Web 4.1 types of societies; Web theoretical perspectives in sociology generally divide into macro and micro views. Web as you probably realize by now, most theories and discussions of socialization concern childhood.
The Major Components Of Social Structure Include Culture, Social.
4.3 social constructions of reality; Web it includes the process by which a society, culture, or group teaches individuals. Which of the following fictional societies is an example of a pastoral society? However, socialization continues throughout the several stages of the life course, most commonly.
Conflict, Cooperation, And Competition 2.
Web this chapter examines several aspects of socialization. Web according to the homeless woman, hilda, what did md stand for? Lenski's term for the changes that occur as society gains new technology. A perception of yourself based on others obsevations.
In So Doing, It Continues Developing The Sociological Perspective Addressed By The Previous Chapters, As We Will Again See The Ways In Which Our Social.
Web social learning theory people learn new attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors through social interactions, especially during childhood role models people we admire and whose behavior we imitate influential in. Web 4.1 types of societies. 4.2 theoretical perspectives on society; Functionalism emphasizes the functions that social institutions serve to ensure the ongoing stability of society, while conflict.