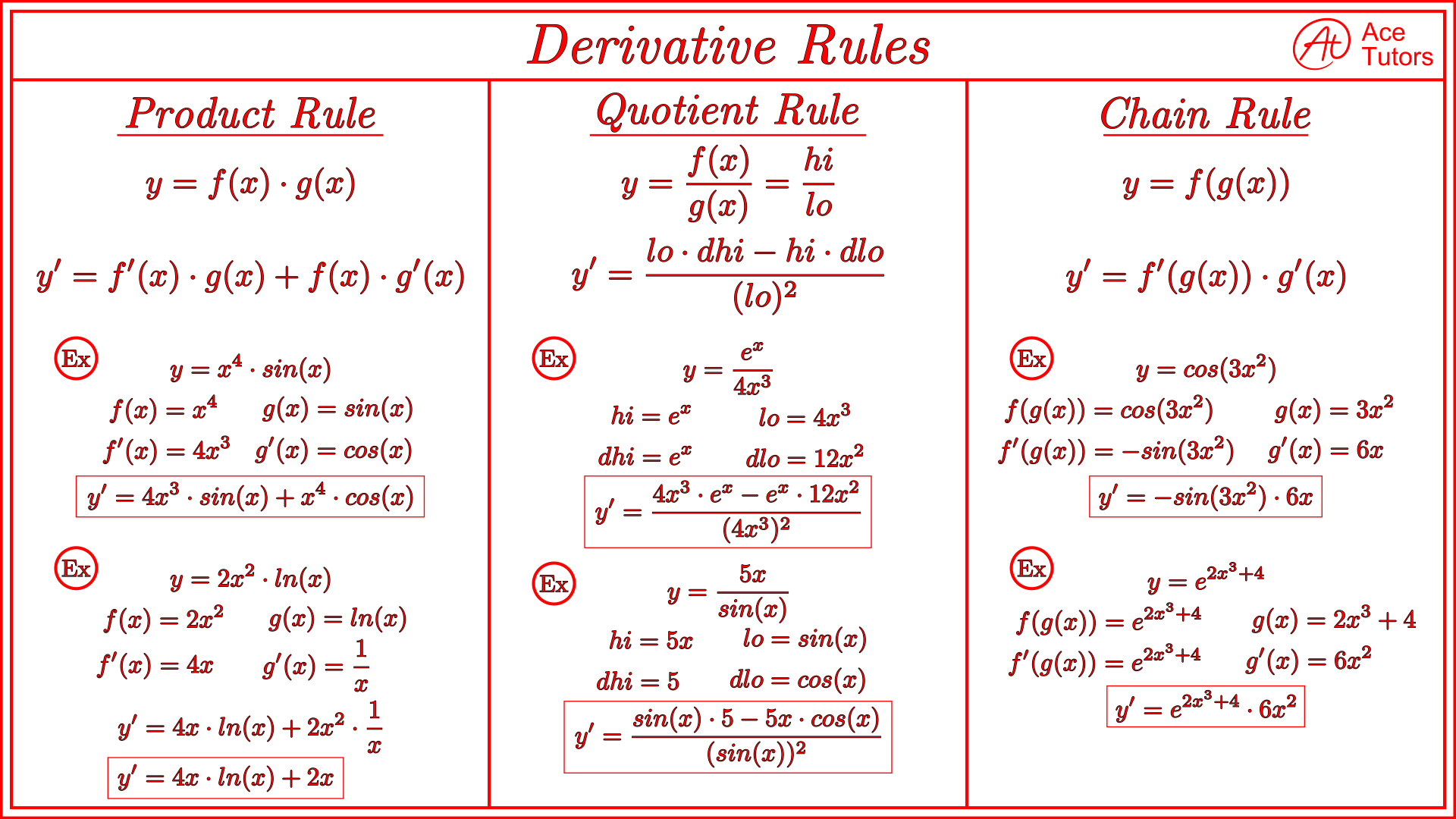
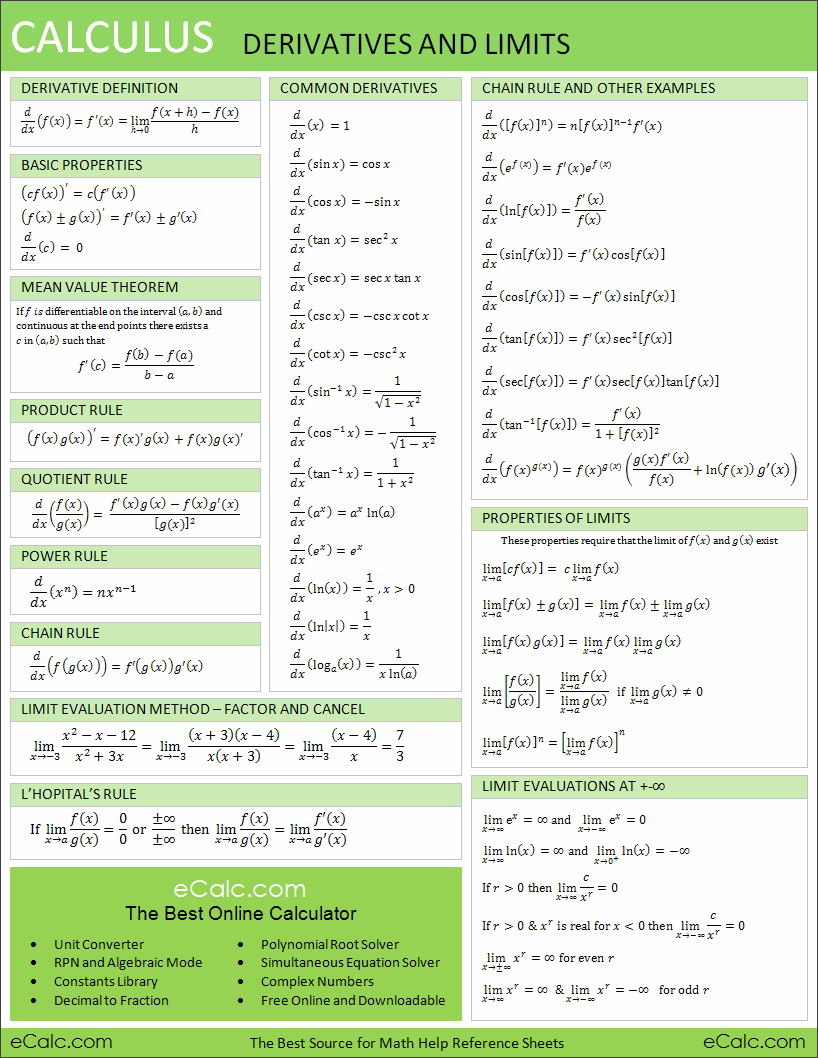
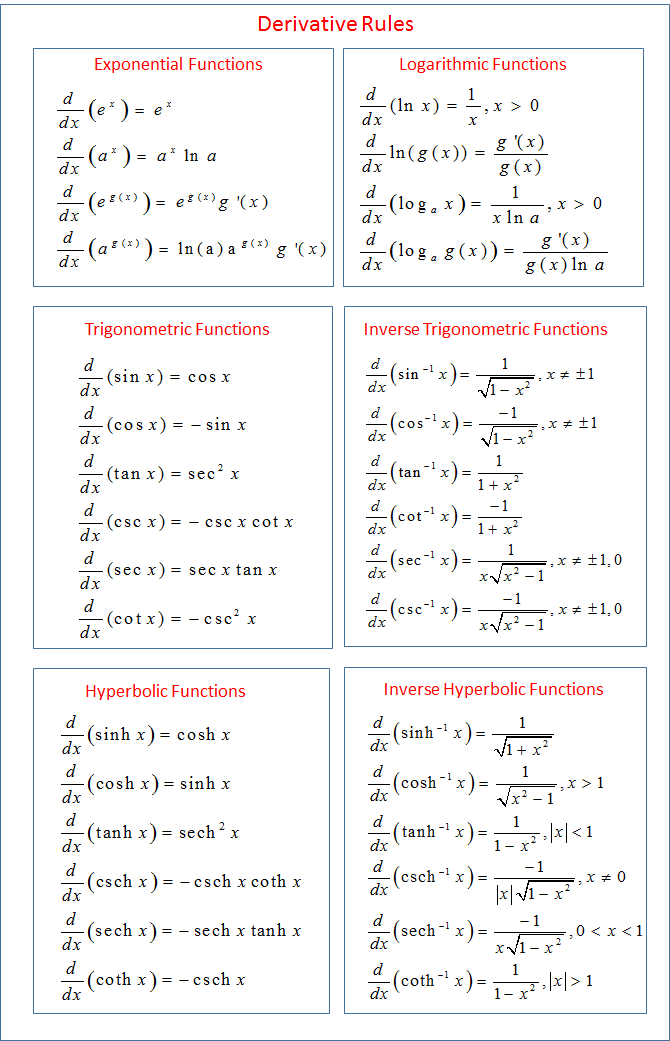
Derivative Shortcut Sheet
Derivative Shortcut Sheet - C are constants, with b > 0. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). D dx (c) = 0; Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. F g 0 = f0g 0fg g2 5. Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. Web derivative and antiderivative shortcuts notes: (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4. D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3.
C are constants, with b > 0. Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3. Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. Web derivative and antiderivative shortcuts notes: Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). F g 0 = f0g 0fg g2 5. D dx (c) = 0;
D dx (c) = 0; Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: F g 0 = f0g 0fg g2 5. Where c is a constant 2. D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3. Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. C are constants, with b > 0. Web derivatives cheat sheet derivative rules 1. (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case).
derivative shortcuts review YouTube
Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: D dx (c) = 0; Web derivative and antiderivative shortcuts notes: D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3.
Derivative Shortcut Rules Rule 7 and Examples YouTube
F g 0 = f0g 0fg g2 5. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). Web derivatives cheat sheet derivative rules 1. D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3. (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4.
Differentiation Rules
D dx (c) = 0; D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3. F g 0 = f0g 0fg g2 5. Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4.
3 3 1 Derivative Shortcuts YouTube
Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family.
Derivative Shortcut Rules Rules 5 and 6 YouTube
Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:. C are constants, with b > 0. Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. Where c is a constant 2. (fg)0 =.
Derivatives Part II You Mean There Was Shortcut This Whole Time
D dx (c) = 0; Where c is a constant 2. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. C are constants, with b > 0.
Derivatives shortcut YouTube
Where c is a constant 2. F g 0 = f0g 0fg g2 5. • we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). D dx (c) = 0; (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4.
Math Cheat Sheets Математикийн Шипи I CAME EARTH FOR EXP
• we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). Web derivatives cheat sheet derivative rules 1. Web derivative and antiderivative shortcuts notes: D dx (c) = 0; Web derivative shortcuts the basic three:
Calculus Derivative Rules (formulas, examples, solutions, videos)
(fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4. Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. C are constants, with b > 0. Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4.
F G 0 = F0G 0Fg G2 5.
Web derivative and antiderivative shortcuts notes: Web derivative shortcuts the basic three: Similarly for in this table, and • a, b, c, g and h. D dx (c) = 0;
C Are Constants, With B > 0.
• we use f(x) (capital) to represent the family of antiderivatives of a function f(x) (lower case). (fg)0 = f0g +fg0 4. Where c is a constant 2. Type f (x) f '(x) text section power xp pxp−1 3.1 exponential bx ln(b)⋅bx 3.1 exponential (special case) ekx kekx 3.1 trig sin(x) cos(x) 3.4 trig cos(x) −sin(x) 3.4 the five ways:.
Web Derivatives Cheat Sheet Derivative Rules 1.
D dx (xn) = nxn 1 3.