What Do The Letters In Dna Stand For
What Do The Letters In Dna Stand For - [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. They have short and easy to remember names: Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine. In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger rna by rna. Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. Web deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) updated: Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. January 12, 2024 definition 00:00.
In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an. They have short and easy to remember names: [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger rna by rna. January 12, 2024 definition 00:00. Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) updated: Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers.
Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. Web under the commonly used iupac system, nucleobases are represented by the first letters of their chemical names: Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an. January 12, 2024 definition 00:00. Web deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) updated: In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine.
What Does DNA Stand For? Do You Know The Answer? Dna, Dna research
Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an. January 12, 2024 definition 00:00. [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger rna by rna.
what do the letters DNA stand for? Brainly.ph
Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. In transcription, the codons of a gene.
What Do The Letters Dna Stand For Thankyou Letter
Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger rna by rna. January 12, 2024 definition 00:00. [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an.
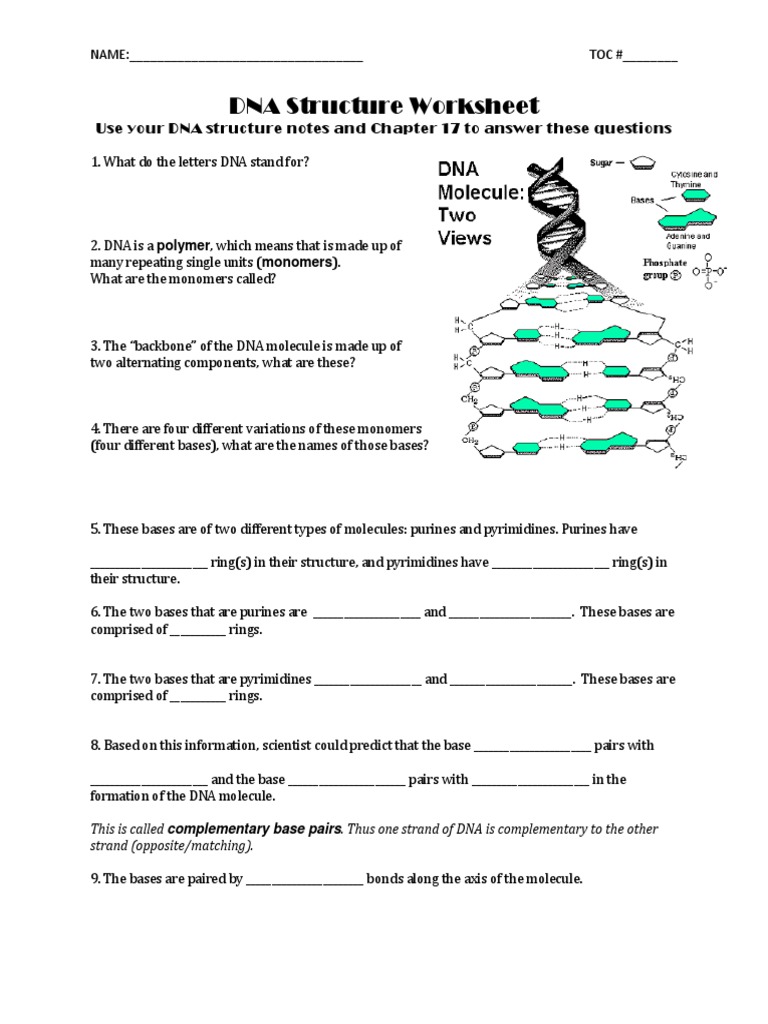
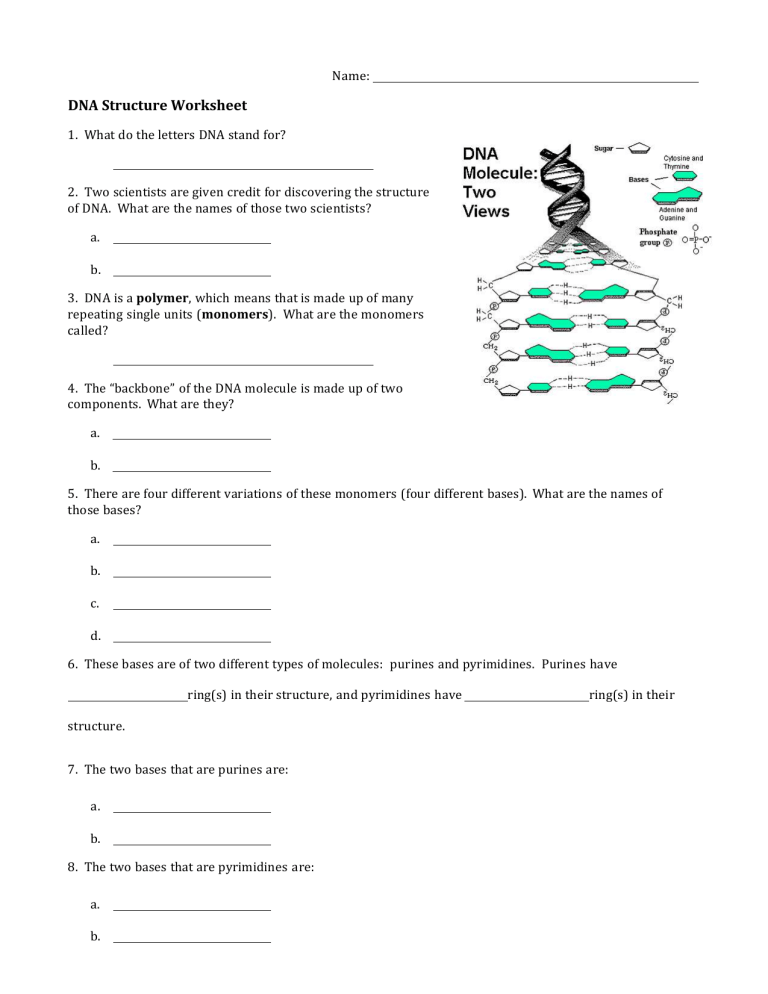
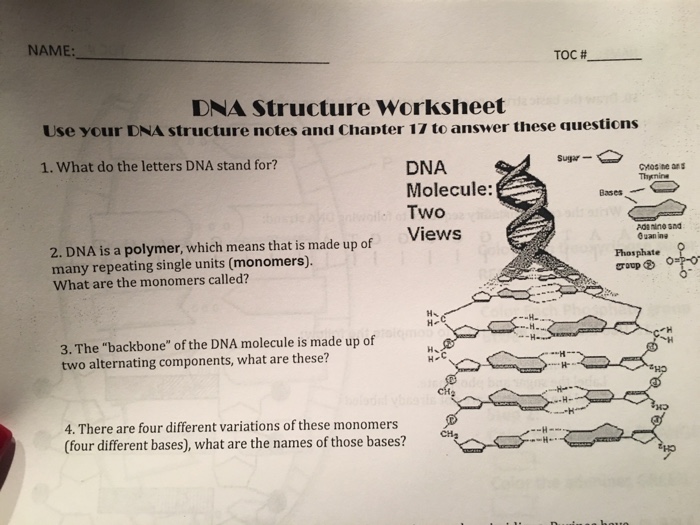
DNA Structure Worksheet
In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger rna by rna. [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine. They have short and easy to remember names: In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other.
What Do The Letters Dna Stand For Thankyou Letter
They have short and easy to remember names: January 12, 2024 definition 00:00. Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. Web under the commonly used iupac system, nucleobases are represented by the first letters.
What do the letters DNA stand for DNA is a polymer, which means tha.pdf
Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. Web under the commonly used iupac system, nucleobases are represented by the first letters of their chemical names: Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria,.
What Does Dna Stand For And How Do You Pronounce It What Does
Web under the commonly used iupac system, nucleobases are represented by the first letters of their chemical names: Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. They have short and easy to remember names: In.
Fantastic What Do The Letters Dna Stand For Shirt, Hooodie, Vneck
[1] this shorthand also includes eleven. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an. Web deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) updated: Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine.
What Do The Letters Dna Stand For Thankyou Letter
Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: [1] this shorthand also includes eleven. In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger.
What Do the Letters DNA Stand for? Free Expert Q&A bartleby
Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine. January 12, 2024 definition 00:00. In transcription, the codons of a gene are copied into messenger rna by rna. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an. Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts:
In Transcription, The Codons Of A Gene Are Copied Into Messenger Rna By Rna.
Each nucleotide monomer is built from three simple molecular parts: Web deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) updated: In any organism, every cell has the same base sequence as every other. Deoxyribonucleic acid (abbreviated dna) is the molecule that carries genetic information for the development and functioning of an.
Web Under The Commonly Used Iupac System, Nucleobases Are Represented By The First Letters Of Their Chemical Names:
Web in contrast, the dna “alphabet” has only four “letters,” the four nucleotide monomers. They have short and easy to remember names: Guanine, cytosine, adenine, and thymine. Web remember, dna stands for deoxyribose nucleic acid and is the repository of all bacteria, plant, and animal hereditary information.
[1] This Shorthand Also Includes Eleven.
January 12, 2024 definition 00:00.